Early Warning Signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis
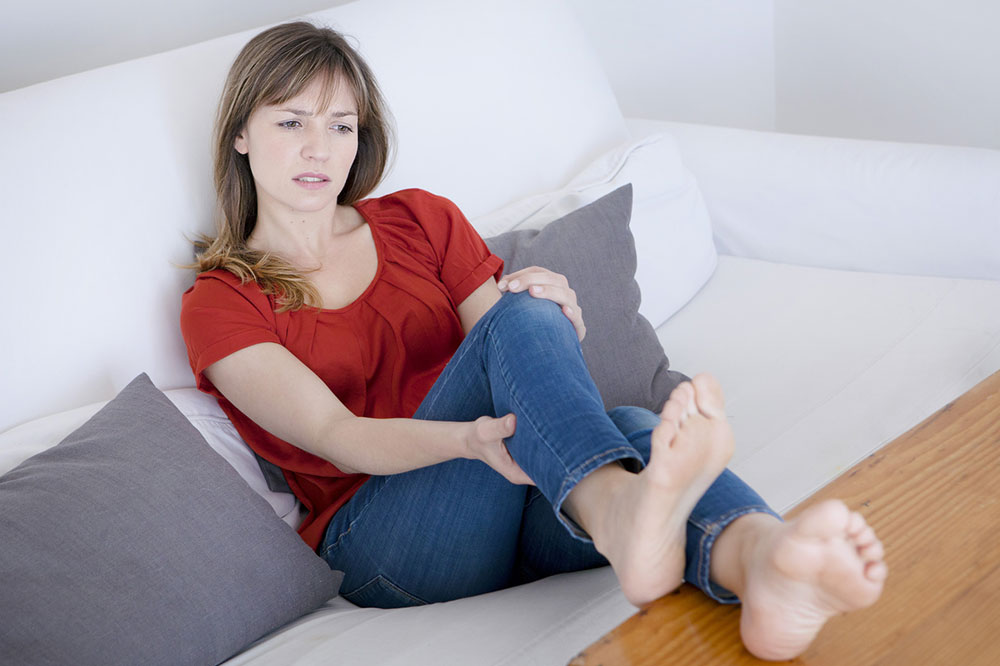
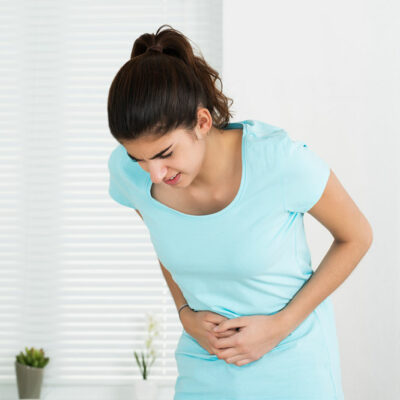
Deep vein thrombosis is a condition in which a blood clot forms in one or more veins, most commonly in the legs. In some cases, the condition might not cause any symptoms, while it may lead to swelling and pain in the legs in other cases. Here are some other telltale symptoms of deep vein thrombosis that require medical attention. 1. Warning signs and telltale symptoms of deep vein thrombosis The symptoms of deep vein thrombosis are caused due to obstruction in blood flow, leading to the accumulation of blood in the veins, especially of the legs. The symptoms can include: Swelling in the legs A crucial symptom of deep vein thrombosis that should be taken seriously is swelling in the legs. Swelling associated with this condition can affect one or both legs. Tenderness or pain Another telltale symptom of deep vein thrombosis is a feeling of tenderness or pain in the ankle, foot, leg, or arm. The pain might feel like a cramp that does not subside. The pain in the leg or feet might only be experienced when one walks or stands. Change in affected skin’s color and temperature The affected area can start feeling warm. Apart from the pain, the skin around the affected area can become red or dark, and the veins in the area will become swollen and hard.
Learn More